TSTool / Datastore Reference / Colorado HydroBase
- Overview
- Standard Time Series Properties
- Limitations
- Datastore Configuration File
- Troubleshooting
- Available Time Series by Data Type Categories
- Database Views
- Database Stored Procedures
Overview
This appendix describes the HydroBase datastore, which is being phased in to replace the HydroBase “input type”.
Installing HydroBase
HydroBase is distributed as a SQL Server Express database. See the following links for the database installer, archive of the databases, and other useful information.
- OpenCDSS HydroBase Product web page
- HydroBase Installation Instructions
- HydroBase Installer download link, which includes:
- SQL Server Express
- HydroBase Database Manager (used to attach downloaded HydroBase databases to SQL Server database software) - the
program installs by default as
C:\Program Files (x86)\Division of Water Resources\HydroBase Database Manager\HydroBaseMaintenanceUtility.exeand can be run to attach downloaded HydroBase databases to SQL Server Express - current CDSS version of TSTool
- does not include HydroBase snapshot - see below to download snapshots
- HydroBase snapshots
- run the HydroBase Database Manager to attach the downloaded database
- a recent snapshot should typically be used since it contains the most up to date data
- older versions are useful for software testing
- datastores can be defined to connect to multiple databases at the same time
- See the TSTool Troubleshooting documentation if HydroBase issues occur.
Database Contents
The State of Colorado’s HydroBase database stores a variety of time series data. The time series conventions described here, in particular for time series identifiers, are consistent for major CDSS software components including TSTool, StateDMI, StateView/CWRAT, and StateMod GUI. This allows for consistent features and sharing of data between software tools.
The current database design splits time series into three main categories:
- Data related to structures or administrative data maintained by the State of Colorado (e.g., diversions, reservoirs). Structure locations are typically identified using a water district identifier (WDID), consisting of a two-digit State of Colorado water district number and a trailing structure identifier (which in the past was four digits but has been increased to five or more digits to support longer identifiers). Although a single WDID identifier is used when identifying time series, the separate WD and ID fields are generally also available in HydroBase.
- Data for stations, consisting mainly of location information and time series (e.g., NOAA precipitation data, USGS streamflow). Station locations are typically identified using a station identifier from the data source. For example, stations can use a USGS identifier, a State of Colorado Satellite Monitoring System abbreviation, or other identifier.
- Data recorded at locations that are not stations or structures. For example, well permits that do not have WDID identifiers and county data such as agricultural statistics.
A structure or station may have more than one identifier depending on the number of agencies involved with data collection, etc. For example, a reservoir may have a State of Colorado WDID because it has water rights, a Bureau of Reclamation identifier, a US Geological Survey identifier, and a second State of Colorado identifier corresponding to a real-time data station. HydroBase collects data from many sources; however, the State has not attempted in all cases to cross-references the identifiers. For example, a streamflow station may have a partial time series record with a “USGS” data source and identifier and a partial time series record with a “DWR” (Division of Water Resources) data source and identifier – the user must recognize that this may be the same station, under different management at different times.
HydroBase downloads are updated for release to the public at least once per year, although internal updates occur year-round. Time series are used with CDSS (Colorado's Decision Support Systems) applications and follow basic time series standards when used by TSTool and other software. See the Available Time Series by Data Type Categories section for a list of available time series.
Database Connections
The newer datastore design is more flexible than older input type design. The HydroBase datastore is a direct database connection that requires installing HydroBase on a local computer (such as for StateCU and StateMod modelers) or server that is accessible in a local network (such as for State of Colorado offices). This datastore provides the fastest performance and most flexibility when processing HydroBase data because the ColoradoHydroBaseRest web service datastore is limited by internet technologies performance and may not provide services for all HydroBase database tables and views.
Some issues remain before moving completely to the datastore concept and consequently the configuration of a HydroBase datastore is an optional feature that is not enabled by default. To enable, it is recommended to:
- Copy the installation datastore configuration file (
C:/CDSS/TSTool-NN.NN.NN/datastores/HydroBase.cfg) to user datastore configuration file (C:/Users/user/.tstool/NN/datastores/HydroBase.cfg). The configuration file distributed with the software usesEnabled=Falseso it will not result in a database connection. This only needs to be done for each major TSTool version (first number in version). - In the user configuration file (
C:/Users/user/.tstool/NN/datastores/HydroBase.cfg):- Comment out the
Enabled=Falseproperty or change toEnabled=True. - Edit the
DatabaseName=HydroBase_CO_YYYYMMDDproperty to match the HydroBase version that has been installed with HydroBase Database Manager tool. The connection to this database will be made automatically when TSTool starts. If the configuration is incorrect, see View / Datastores for troubleshooting information. This connection is independent of the HydroBase selector dialog shown at startup. Use the HydroBase selector to list HydroBase names that are available. See also the Datastore Configuration File section.
- Comment out the
The database selected with the HydroBase selector when TSTool starts results
in a separate database connection using the cdss login (HydroBase logins are explained below) and is listed as an Input type.
Commands such as ReadHydroBase and time series identifiers ending in ~HydroBase will first
search for a datastore named HydroBase and if not found will use the database connection
from the selector dialog (input type).
Consequently, a HydroBase datastore will take precedence over the database connection
from the interactive HydroBase selection at TSTool startup.
Technical issues with fully moving to datastore include how to change the traditional HydroBase login dialog and implement best practices for naming datastores when dealing with dated versions of HydroBase.
The HydroBase database contains stored procedures and views suitable for the following users (accounts):
- CDSS user (SQL Server login
cdss, passwordcdss%tools) - is a service account that exposes HydroBase data through stored procedures and views appropriate for decision support system projects. HydroBase CDSS view names have the prefixvw_CDSS(e.g., structures are in a view or tablevw_CDSS_Structure). This is the default account when using the HydroBase datastore. - HBGuest user (SQL Server login
HBGuest, password1HBGuest) - is a read-only service account that exposes HydroBase data through stored procedures and views appropriate for general database users. HydroBase HBGuest view names do not have the prefixvw_CDSS(e.g., structures are in a view or tablestructure). See the HBGuest User Manual for an overview of HBGuest configuration and database access.
A general rule of thumb is that the CDSS account should be used for full TSTool functionality;
however, the HBGuest account can be used to query views that are not available via the
CDSS account (e.g., the vw_HBGuest_StructureAssocWDID table provides
information about augmentation plans and other structure groups).
TSTool connections for the above HydroBase accounts can be figured in several ways. Refer to the recommended approach at the top of this section and details in the Datastore Configuration File section.
- CDSS user:
- Configure as the HydroBase “input type”. This is the default legacy behavior when HydroBase is enabled, and relies on the user selecting a HydroBase database via the HydroBase selection dialog. This approach may be phased out in the future in favor of the more generic datastore approach.
- Configure a HydroBase CDSS datastore using a HydroBase datastore configuration file. If the datastore name is configured as “HydroBase”, this connection will supersede the “input type” when encountered in time series identifiers. The account will default to the CDSS service account. An example configuration file is shown in the Datastore Configuration File section below.
- Configure a HydroBase CDSS datastore using a configuration file with an ODBC DSN.
In this case, the ODBC DSN must be configured using a SQL Server driver
with login
cdssand passwordcdss%tools. An example configuration file is shown in the Datastore Configuration File section below.
- HBGuest user:
- Configure a Generic Database datastore using a HydroBase datastore configuration file. See the Datastore Configuration File section below). This approach may be needed if the ODBC DSN configuration (next item) results in errors, and the text configuration file may be more transparent than the ODBC DSN.
- Configure a HydroBase datastore using a configuration file with an ODBC DSN. In this case, the ODBC DSN must be configured using a SQL Server driver with login HBGuest and password 1HBGuest. See the example for the CDSS account in the Datastore Configuration File section below.
Versioning
The HydroBase version is indicated by the date in the distribution file and database instance name.
For example, the HydroBase database instance name HydroBase_CO_20210322 indicates that HydroBase has a release date 20210322.
Internally, the HydroBase design has a date that is different than the release date.
However, for all practical purposes, using the release date also implies the database design date.
TSTool examines the database structure to confirm the version and is able to handle multiple database versions.
The # Comment @require datastore syntax
requires using a date string with format YYYYMMDD (e.g., 20210322),
which corresponds to the HydroBase instance (release) date.
Standard Time Series Properties
The standard time series identifier format for HydroBase datastore time series is of the form:
Location.DataSource.DataType.Interval~DataStoreName
Due to the variety of data types, sources, and formats in HydroBase, time series properties can be set a number of ways. General guidelines are as follows:
- The location part of the time series identifier is set to a station or structure identifier, which is typically the identifier used by the managing agency. For example, USGS stream gages use the 8-digit USGS identifier and State of Colorado diversions use a 7-character zero-padded structure WDID (water district identifier). Wells often use the latitude and longitude merged together (see additional comments in the wells section).
- The source part of the time series identifier corresponds to a data provider abbreviation. For example, if the current provider for a time series is the USGS, then the data source will be USGS. If the State of Colorado has at some point taken over maintenance of a station from the USGS, then the data source will be DWR. Individual data records may indicate a variety of data sources. The convention in HydroBase is to store the data records under the current data source, rather than force the user to query more than one time series and merge the time series. If, however, a station has moved, then separate time series typically will be available, likely under different identifiers. For this reason, the location of the station or structure is important in understanding historical records.
- The data type part of the time series identifier as much as possible uses the
“measurement type” information in HydroBase or a readable and reasonable data type phrase.
For example
Precipis a measurement type for station data andDivTotal(diversion total) is a measurement type for diversion data. In some cases, especially with real-time data, the data type may not exactly match HydroBase. For example, HydroBase uses a measurement typeRT_Ratefor multiple stream related data types. TSTool uses a data type of Streamflow. The tables at the end of this appendix describe all available HydroBase data types and provides guidance for upgrading from old data types. - Data intervals are set based on the tables that are being queried.
In most cases, a regular interval like
DayorMonthis used.Irregularis used for real-time data because there currently is no way to know without doubt what the regular data interval is (e.g.,15MIN). Data that are measured infrequently (e.g., reservoir field measurements) typically are stored as a regular interval time series with intervalDay. This allows more flexibility in data processing and filling. - In older versions of TSTool, the scenario part of the identifier (after the interval)
was sometimes used to supplement the data type information.
For example, real-time flow data in the database has a number of attributes (
Streamflow,RT_Rate,DISCHRG) that cannot easily fit into the standard time series identifier. The current version of TSTool usesdatatype-subdatatypewhere necessary and generally does not use the scenario for normal time series identifiers (WIS time series are an exception) and this field is being reserved to possibly indicate historical data, filled data, etc. - Units are set based on the database table definitions.
- Period of record is set based on the available database contents. Periods displayed when listing stations and time series typically are not determined by checking the data because this would require querying large amounts of data. Instead, periods are determined from summary information available in the database. In some cases, the period of record information is not saved at a precision sufficient to accurately represent the true period (e.g., the database may indicate data for years but not months). Therefore, the true period will only be available when time series data values are queried.
- Missing data typically are set to
-999in time series but are stored as nulls in the database. TSTool does allowNaN(not a number) to be used but-999continues to be used to match legacy conventions. - The input type of the time series identifier is set to the datastore name, which typically is HydroBase for a default connection. If multiple HydroBase connections are needed, the datastore configuration information is used to assign an appropriate name.
- The time scale for data (whether accumulated [
ACCM], instantaneous [INST], or mean [MEAN]) is not automatically determined from the data type and interval but must be understood from the data type.
Diversion data may be retrieved from several tables in HydroBase,
including daily and monthly detailed records, infrequent values, diversion comments, and currently in use values.
The TSTool ReadHydroBase
command provides several options for handling data and the
FillUsingDiversionComments
command can be used to fill with additional zero values.
When using time series identifiers to read time series, the following defaults are used:
- Daily
DivClassandDivTotaltime series are filled using the carry-forward technique implemented by the State of Colorado. Missing irrigation years remain missing. Years with data are filled with zeros at the start and values are carried forward until another observation is found, or to the end of the irrigation year. - Diversion comments and “currently in use” flag are NOT automatically applied. This default may change in the future but is retained for historical data processing reasons.
Limitations
HydroBase has the following limitations related to time series storage:
- The station and structure measurement types and time series tables defined in HydroBase
do not always allow information to be determined from database records.
Instead, some time series properties must be hard-coded based on the table design.
For example, the
meas_typetable has aMeanTemp,MaxTemp,MinTemptypes defined, but these refer primarily to the separate daily tables for such data. Themonthly_temptable includesavg_max_t,avg_min_t, andmean_tcolumns that do not correspond one-to-one withmeas_typevalues. Therefore, applications like TSTool use data types that are not specifically defined as strings in HydroBase, which have consequently been hard-coded. This is an issue with station and structure time series. - Real-time data types in HydroBase do not directly translate to time series data types used in TSTool. An effort has been made to be as consistent as possible while using data types that can be understood by users.
- Data units are not defined consistently in tables.
Some tables have a units string and others do not and the units abbreviations are
not always consistent (units of
Aare often used for acre-feet andCforCFS). A master units table is not used in HydroBase to enforce data units consistency throughout the database. - The time scale for time series (whether accumulated, instantaneous, or mean) is not automatically determined from the data type and interval. Users much understand how to interpret the data, in particular when changing the data interval.
Datastore Configuration File
A datastore is configured by enabling HydroBase features in the main TSTool.cfg configuration
file and creating a datastore configuration file for each connection.
Configurations are processed at software startup to enable datastores.
An example of the TSTool configuration file is shown below.
Use the HydroBaseEnabled property to enable/disable HydroBase features in TSTool,
such as commands shown in interface menus.
Multiple datastores can be configured.
Properties for each datastore are specified in an
accompanying configuration file described after the following example.
# Configuration file for TSTool
[TSTool]
HydroBaseEnabled = true
TSTool Configuration File with HydroBase Properties
HydroBase Datastore Using CDSS Account
The following illustrates the HydroBase datastore configuration file format for the CDSS account. The configuration file is typically named as follows:
C:\CDSS\TSTool-Version\datastores\HydroBase.cfg- installation HydroBase datastore configurationC:\Users\user\.tstool\NN\datastores\HydroBase.cfg- user's HydroBase datastore configuration
The default cdss service account is used for authentication and allows read-only access to the database.
# Configuration information for HydroBase database datastore, CDSS account.
#
# The user will see the following when interacting with the datastore:
#
# Name - datastore identifier used in applications, for example as the
# input type information for time series identifiers (usually a short string)
# Description - datastore description for reports and user interfaces (short phrase)
#
# The following are needed to make database connections in the software
#
# Type - must be HydroBaseDataStore
# DatabaseEngine - the database software (SqlServer is current standard)
# DatabaseServer - IP or string address for database server, with instance name
# (e.g., "localhost\CDSS" can be used for local computer). Omitting
# the instance name will result in default port numbers being tried
# until one works.
# DatabaseName - database name used by the server (e.g., HydroBase_CO_20120722)
# SystemLogin - service account login (omit for default)
# SystemPassword - service account password (omit for default)
# Enabled - if True then datastore will be enabled when software starts, False to disable
Type = "HydroBaseDataStore"
Name = "HydroBase"
Description = "HydroBase Datastore"
DatabaseEngine = "SqlServer"
# Local SQL Server Express installation...
DatabaseServer = "localhost\CDSS"
# Or a specific server...
#DatabaseServer = "amazon\CDSS"
DatabaseName = "HydroBase_CO_20120722"
HydroBase Datastore Configuration File for Default CDSS Account (no ODBC DSN)
HydroBase Datastore Using CDSS Account and ODBC DSN
The following illustrates the HydroBase datastore configuration file format for the CDSS account using an ODBC DSN.
The configuration file is located in the same folder as the TSTool configuration file and
configures a datastore named HydroBase-DSN.
The ODBC DSN generally is configured using SQL Server authentication and the cdss account information.
If for some reason HydroBase did not fully install resulting in accounts not being configured,
then Windows authentication can be used.
Using an ODBC DSN can be problematic if the ODBC driver, authentication, method,
or other SQL Server configuration information is in error.
# Configuration information for HydroBase database datastore, CDSS account, using ODBC DSN.
#
# The user will see the following when interacting with the datastore:
#
# Name - datastore identifier used in applications, for example as the
# input type information for time series identifiers (usually a short string)
# Description - datastore description for reports and user interfaces (short phrase)
#
# The following are needed to make database connections in the software
#
# Type - must be GenericDatabaseDataStore
# DatabaseEngine - the database software (SqlServer is current standard)
# OdbcName - the Open Database Connectivity Data Source Name (ODBC DSN), configured
# in Windows Control Panel
# Enabled - if True then datastore will be configured when software starts, False to disable
Enabled = True
Type = "HydroBaseDataStore"
Name = "HydroBase-DSN"
Description = "HydroBase Datastore using ODBC DSN"
DatabaseEngine = "SqlServer"
OdbcName = "HydroBase-DSN"
# Yse the following to set additional SQL Server driver properties, used for troubleshooting
#ConnectionProperties = "SomeProp=Value;SomeProp=Value"
HydroBase Datastore Configuration File for CDSS Account Using ODBC DSN
The above approach may result in database query errors in the TSTool log file:
Connection is busy with results for another command
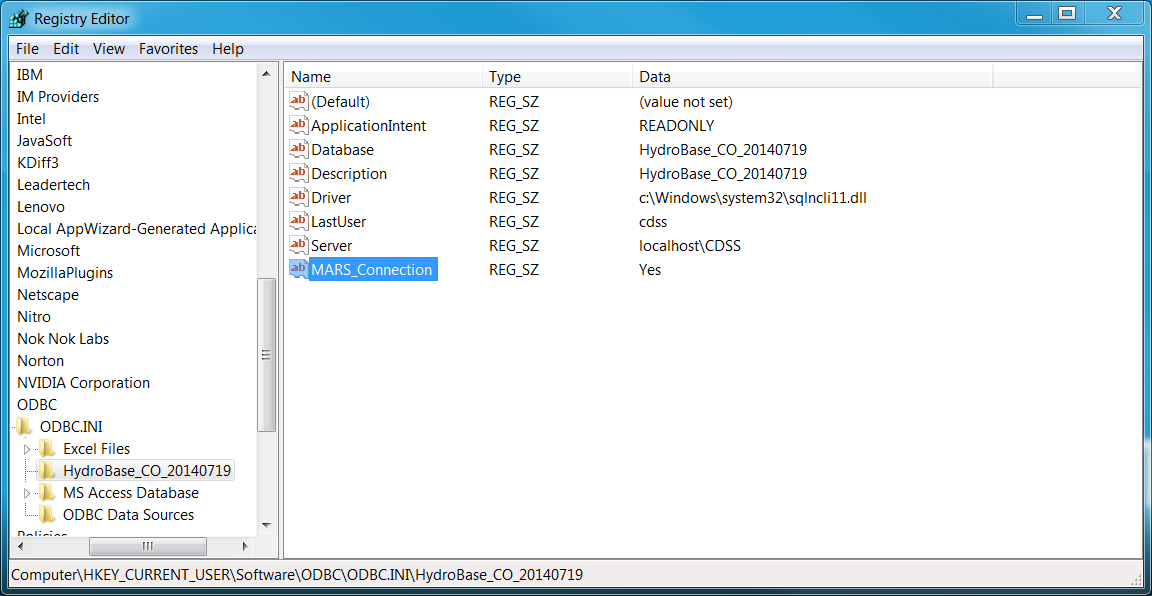
In this case it is necessary to edit the registry with the regedit program as follows solved the problem.
Search for the ODBC name that was assigned to find the registry settings to edit.
An attempt was made to determine how to set the property in the connection URL but no documentation could be found.
See the following for background. See also the full-size image.
HydroBase Datastore Using HBGuest Account and Generic Database Datastore
The following illustrates the Generic Database datastore configuration file format
for the HBGuest account NOT using an ODBC DSN (see also the Generic Database Datastore appendix.
The configuration file is located in the same folder as the TSTool configuration file and
configures a datastore named HydroBase-HBGuest.
The HBGuest service account is used for authentication and allows read-only access to the database.
# Configuration information for HydroBase database HBGuest datastore,
# using generic database datastore.
#
# The user will see the following when interacting with the datastore:
#
# Name - datastore identifier used in applications, for example as the
# input type information for time series identifiers (usually a short string)
# Description - datastore description for reports and user interfaces (short phrase)
#
# The following are needed to make database connections in the software
#
# Type - must be GenericDatabaseDataStore
# DatabaseEngine - the database software (SqlServer is current standard)
# DatabaseServer - IP or string address for database server, with instance name
# (e.g., "localhost\CDSS" can be used for local computer)
# DatabaseName - database name used by the server (e.g., HydroBase_CO_20120722)
# SystemLogin - service account login (specify for HBGuest account)
# SystemPassword - service account password (specify for HBGuest account)
Enabled = True
Type = "GenericDatabaseDataStore"
Name = "HydroBase-HBGuest"
Description = "HydroBase HBGuest Datastore"
DatabaseEngine = "SqlServer"
# Local SQL Server Express installation...
DatabaseServer = "localhost\CDSS"
DatabaseName = "HydroBase_CO_20121126"
# Specify HBGuest login...
SystemLogin = "HBGuest"
SystemPassword = "1HBGuest"
Generic Database Datastore Configuration File for HydroBase HBGuest Account
Troubleshooting
The following table lists errors that may result from connecting to or using HydroBase, and potential solutions to address the errors. See also the main TSTool Troubleshooting section.
HydroBase Connection Errors and Possible Solutions
| Error | Possible solutions |
|---|---|
| A HydroBase datastore configuration generates errors. |
|
| A specific requested time series is not returned from the HydroBase database. | Time series in HydroBase are associated with the data source (e.g., USGS). These data source abbreviations or their handling by software may have changed over time and a data source in a time series identifier may not be valid. Current software requires the data source for HydroBase time series, if a data source is used with the data type in HydroBase. Try interactively querying the time series to see if the data source has changed. |
Available Time Series by Data Type Categories
The following tables present a summary of time series identifier fields for the HydroBase data types. Data sources may be added and/or removed with data updates. Data types are listed by major group and are alphabetized by the data type description within the group. The time scale is provided to facilitate data use, in particular when changing the time interval.
Agricultural Crop and Livestock Data
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural/ CASS | Colorado Agricultural Statistics Service crop area harvested | County Name | CASS |
CropAreaHarvested-Commodity_PracticeCommodity and practice are from available values in HydroBase. |
Year INST |
See NASS data for orchards, pasture, and vegetables. Perennial crops usually have only harvested value. |
| CASS area planted | County Name | CASS |
CropAreaPlanted-Commodity_PracticeCommodity and practice are from available values in HydroBase. |
Year INST |
Annual crops should have planted value but use maximum of planted and harvested if necessary. | |
| CASS livestock head | County Name | CASS |
LivestockHead-Commodity_TypeCommodity and type are from available values in HydroBase. |
Year INST |
For each commodity (e.g., sheep), multiple types (e.g. sheep at various maturity levels). | |
| Agricultural/ GIS | CDSS irrigated lands assessment result. See also Diversion Comments below. |
WDID |
CDSSGIS |
CropAreaAllIrrigation-CropTypeCropAreaDrip-CropTypeCropAreaFlood-CropTypeCropAreaFurrow-CropTypeCropAreaSprinkler-CropTypeCropType is taken from available values in HydroBase. |
Year INST |
Data are only available for years where DSS projects or data refreshes have occurred. Partial data for intermediate years may be available in spatial data layer attributes but not HydroBase. Data are available for lands served by surface water structures, listed by crop/year/irrigation type. |
| Agricultural/ NASS | CropArea |
County Name | NASS |
CropArea-CommodityCommodity is taken from available values in HydroBase. |
Year INST |
See CASS data where available. NASS does not distinguish between planted and harvested. NASS data are useful for orchards, pasture, and vegetables, which may not be reported in CASS. |
Climate Data
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | Evaporation (Pan) | Station ID | NOAA |
EvapPanOld (obsolete) data type was EPAN. |
Day ACCM,Month ACCM |
|
| Frost Dates (derived from temperatures) |
Station ID | COAGMNOAA |
FrostDateL28S,FrostDateL32S,FrostDateF28F,FrostDateF32FOld (obsolete) data type was FrostDate or FrostDates. |
Year INST |
Time series in software are the Julian day of the year (1-366) to allow graphing, filling, and manipulation. | |
| Precipitation | Station ID | COAGMNOAA |
PrecipOld (obsolete) data type was PTPX. |
Day ACCM,Month ACCM,Irregular ACCM |
Irregular data are real-time increments. | |
| Snow (accumulation on ground during interval). | Station ID | NOAA |
SnowOld (obsolete) data type was SNOG. |
Day ACCM,Month ACCM |
||
| Snow course depth and snow water equivalent | Station ID | SCS |
SnowCourseDepth,SnowCourseSWEOld (obsolete) data type was SnowCrse, SNWE. |
Day INST |
Values are recorded on a day, with one or more times a month. | |
| Solar radiation | Station ID | COAGM |
SolarOld (obsolete) data type was RADS. |
Day ACCM |
||
| Temperature (instantaneous) | Station ID | various | Temp |
Irregular INST |
||
| Temperature (maximum) | Station ID | COAGM,NOAA |
TempMaxOld (obsolete) data type was MaxTemp, TAMX. |
Day INST |
||
| Temperature (mean of maximum daily values) | Station ID | COAGM,NOAA |
TempMeanMaxOld (obsolete) data type was MaxTemp, TAMX with monthly interval. |
Month MEAN |
||
| Temperature (mean) | Station ID | COAGM,NOAA |
TempMeanOld (obsolete) data type was MeanTemp, TAVG. |
Month MEAN |
||
| Temperature (minimum) | Station ID | COAGM,NOAA |
TempMinOld (obsolete) data type was MinTemp, TAMN. |
Day INST |
||
| Temperature (mean of minimum daily values) | Station ID | COAGM, NOAA |
TempMeanMinOld (obsolete) data type was MinTemp, TAMN with monthly interval. |
Month MEAN |
||
| Vapor pressure (mean daily) | StationID | COAGM |
VaporPressureOld (obsolete) data type was VP, MVP. |
Day MEAN |
||
| Wind run | Station ID | AGRO,COAGM |
WindOld (obsolete) data type was UDIS. |
Day ACCM |
Demographic Data
Demographic data are related to human population. See the Agricultural Data above for livestock population.
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Human population (persons) | Area_type-Area_nameThe type indicates whether a county, municipality, state, etc. The name agrees with the type. The combination defines a unique location. |
(blank) This could be assumed from the Pop_type part of the data type; however, the data source is not readily available in HydroBase. |
HumanPopulation-Pop_typeThe population type is Census, Estimated, etc. |
Year INST |
See CDSS documents for information on how population estimates are determined. |
Diversion Data
See more information after the following table.
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversion May include records for reservoir and well structures, as per State of Colorado administration practices. See also reservoir data. |
Diversion Class (showing water color) | WDID |
DWR |
DivClass-SFUTOld (obsolete) data type was DQME, Div, or Diversion. |
Day MEAN,Month INSTor ACCM,Year INST or ACCM |
SFUT is encoded as:S:s F:f U:u T:ts = sourcef = fromu = uset = typeAnnual values are for irrigation year (Nov-Oct). |
| Diversion Comment (the acreage for a diversion and string data flag indicating whether a structure irrigated in a year) | WDID | DWR |
DivComment |
Year INST or ACCM |
The numerical time series value is set to the acreage for the year. The data quality flag is set to the HydroBase diversion_comment not_used flag. Therefore, this time series can be used to extract total acreage for a structure and determine if diversions should be zero for a year.Annual values are for irrigation year (Nov-Oct). |
|
Diversion Total (sum of all DivClass records for a structure). |
WDID | DWR |
DivTotalOld (obsolete) data type was DQME, Div, or Diversion. |
Day MEAN,Month INST or ACCM,Year INST or ACCM |
Annual values are for irrigation (Nov-Oct) year. |
The above table summarizes how diversion records are available as time series. However, to determine a complete diversion time series, it is necessary to understand the various ways that diversion records can be stored. See also the State of Colorado’s Diversion Record Standard.
Raw data observations for a diversion structure are stored as one or more of the following forms in HydroBase:
- Daily water class time series. These data are recorded using irrigation year (November to October). If one or more values have been entered in a month, then HydroBase will include a full month of data. Days at the beginning of the irrigation year that have no observed values at the start of the year should be considered to be zero, regardless of values found in previous irrigation years. Once an observation occurs, then days within the month where an observation was not recorded are set to the last observed value. Therefore, if an irrigation year contains at least one value, that irrigation year will have at least one month of values (with no missing in the month). To preserve space in HydroBase, months with no observations are not included in the daily data in the database. If a year has no observation, then no data are available in HydroBase for the year and a determination of whether the data values should be zero or other must be determined using other data (see below) or engineering judgment. TSTool and StateView by default implement the carry-forward procedure within irrigation years.
- Diversion comments. Diversion comments may be included for an irrigation year.
The
not_usedflag indicates if a diversion was not used in a year. If this is the case, then daily diversion records should not be available and a zero value can be assumed for the water year. TSTool and StateView DO NOT by default use diversion comments when providing daily or monthly time series. - Infrequent water class. Infrequent water class values can be entered as an annual value for the irrigation year, or as a monthly value. The data can be accessed as time series in TSTool, although no specific capabilities have been implemented to supplement the daily or monthly time series.
Processed (derived) data records are created as follows:
- Daily total diversion. Daily water class values are accumulated to daily total records. Similar to the daily water class, any month that has at least one value will result in a month with no missing data. To preserve space in HydroBase, only months that include an observation are included in HydroBase. Other months in the same irrigation year should be carried forward. Irrigation years with no observation have no records in HydroBase and a determination of whether the data values should be zero or other must be made using other data (see below) or engineering judgment. TSTool and StateView by default implement the carry-forward procedure within irrigation years.
- Monthly water class. Monthly water class is computed by converting the daily water class values (average CFS) to ACFT for each day of the month, and adding the values. Because of the way that daily data are treated, a month will either have all daily values or none. A month with no data will have its value set to missing in the database. Full irrigation years with no observation will result in a full year of missing values, and a determination of whether the data values should be zero or other must be determined using other data (see below) or engineering judgment. Unlike daily data, monthly diversion records are included in HydroBase for the full data period. Full years of missing values may be included in the database.
- Monthly total diversion. This is derived using the same procedure as monthly water class; however, the daily total diversion is used as input.
- Infrequent data are not considered when producing the monthly total time series.
Therefore, to determine a complete time series, the following must be performed, using TSTool or other software:
Daily time series:
- Read the daily time series from HydroBase. The default in TSTool and StateView is now to carry forward daily diversion time series within the irrigation year.
- Utilize the diversion comments to set additional years of data to zero. Using diversion comments is an option with TSTool and StateDMI time series read commands.
- For years with no data, use an appropriate fill technique. If it is known that the ditch did not operate, then zeros should be used. If it is known that the ditch did operate, use historical averages or some other method to fill the data.
- HydroBase infrequent diversions could be used to supplement the data, but currently there is no software to help users with this process.
Monthly time series:
- Read the monthly time series from HydroBase. Any irrigation year with at least one daily observation results in 12 monthly time series values.
- Utilize the diversion comments to set additional years of data to zero. Using diversion comments is an option with TSTool and StateDMI time series read commands.
- For years with no data, use an appropriate fill technique. If it is known that the ditch did not operate, then zeros should be used. If it is known that the ditch did operate, use historical averages or some other method to fill the data.
- HydroBase infrequent diversions could be used to supplement the data, but currently there is no software to help users with this process.
Yearly time series:
- Infrequent time series can be read by TSTool and can supplement the above data. However, currently there is no software to help users with this process. General TSTool commands must be used as appropriate.
Hardware Data
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Battery voltage | Station ID | DWR |
Battery |
Irregular INST |
Limited data are available. This data type allows remote system maintenance checks. |
Hardware data types are not commonly available have been implemented as a test and to allow for greater future use.
Reservoir Data
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir | Field Measurements | WDID | DWR,other |
ResMeasElev,ResMeasEvap,ResMeasFill,ResMeasRelease, |
ResMeasStorageOld (obsolete) data type was RSTO. |
Day INST,Day ACCM,Day ACCM,Day ACCM,Day ACCM |
| Pool Elevation | Station ID or State of CO Abbrev. | DWR,other |
PoolElev |
Irregular INST |
Real-time data for reservoirs are recorded using a station abbreviation that does not match a WDID. | |
| Release Class (showing water color) | WDID | DWR |
RelClass-SFUT |
Day MEAN,Month INST or ACCM,Year INST or ACCM |
SFUT is encoded as:S:s F:f U:u T:ts = sourcef = fromu = uset = typeAnnual values are for irrigation year (Nov-Oct). |
|
| Release Comment (the acreage for a release and string data flag) | WDID | DWR |
RelComment |
Year INST or ACCM |
See DivComment comments. Sometimes acreage is associated with reservoirs. Annual values are for irrigation year (Nov-Oct). |
|
Release Total (sum of all RelClass records for a structure). |
WDID | DWR |
RelTotal |
Day MEAN, Month INST or ACCM, Year INST or ACCM |
Annual values are for irrigation year (Nov – Oct). | |
| Release (instantaneous) | Station ID | DWR,other |
Release |
Irregular INST |
Real-time data for reservoirs are recorded using a station abbreviation that does not match a WDID. | |
| Reservoir Storage (end of month). | WDID | USBR,DWR,other |
ResEOMOld (obsolete) data type was RSTO. |
Month INST |
Few time series are available. | |
| Reservoir Storage (end of year). | WDID | USBR,DWR,other |
ResEOY |
Year INST |
From annual_res table. |
|
| Storage (instantaneous) | Station ID or State of CO Abbrev. | DWR,other |
Storage |
Irregular INST |
Real-time data for reservoirs are recorded using a station abbreviation that does not match a WDID. |
Stream Data
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream | Natural Flow | Station ID | USBR |
NaturalFlowOld (obsolete) data type was Nat_flow, NQME |
Month INST or ACCM |
|
| Stage | Station ID | DWR,other |
Stage |
Irregular INST |
Real-time data. | |
| Streamflow | DWR Abbrev. or USGS station ID | DWR,USGS,other |
StreamflowOld (obsolete) daily, monthly data type was QME. Old real-time data type used RT_rate and scenario DISCHRG or other VAXfield to indicate channel. |
Day MEAN,Month INST or ACCM, Irregular INST |
Real-time data use Irregular time interval. | |
| Streamflow (maximum of daily mean) | Station ID | DWR,USGS |
StreamflowMaxOld (obsolete) data type was Maxq, Maxflow. |
Month INST |
||
| Streamflow (minimum of daily mean) | Station ID | DWR,USGS |
StreamflowMinOld (obsolete) data type was Minq, Minflow. |
Month INST |
||
| Water temperature (instantaneous) | Station ID, State of CO Abbrev. |
DWR,other |
WatTemp |
Irregular INST |
Real-time data, using identifier that does not match USGS or other identifier for historical data. |
Water Information Sheet Data
Water Information Sheets were a feature of CDSS developed for real-time water administration, but are no longer used (typically Excel workbooks are used). The following information is being retained for historical reasons in case it is useful for future system feature design.
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WIS | Water Information Sheet (WIS) cell values, over time | WIS row identifier. For example, structures have an identifier wdid:NNNNNNN, where the leading wdid: is a literal string and the following information is the actual WDID. Similarly, stations start with stat:, followed by a station ID; confluences with conf:, followed by the HydroBase wd_water numbers for the tributary and the larger stream; other row types with othr:, followed by a sequential number in the WIS. |
DWR |
Data types match the WIS columns, as follows:WISPointFlow,WISNaturalFlow,WISDeliveryFlow,WISGainLoss,WISRelease,WISPriorityDiversion,WISDeliveryDiversion,WISTribNaturalFlow,WISTribDeliveryFlow,WISDryRiver(not currently implemented – may be implemented as a data flag in the future). |
Day MEAN |
The scenario part of the time series identifier is set to the sheet name. Over time, WIS with a particular sheet name may be modified in format. The combination of sheet name and row identifier can be used to find data. The time series description is set to the row label. Data values are as stored for the WIS, which reflect the gain method used when the sheet was stored. |
Well Data
See additional information after the following table.
| Data Group | Data Type Description | Location | Data Source | Data Type | Available Intervals and Time Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well | Well level (elevation and depth) | Location identifier, based on the current data source. For example, if the data source is USGS, the location identifier will be the USGS identifier. | various | WellLevel (phasing out in favor of WellLevelElev),WellLevelDepth,WellLevelElev |
Day INST,Irregular INST |
Daily data are historical measurements, often at the ends of a month. A well may have multiple identifiers. However, the identifier presented in TSTool is that corresponding to the primary data source. See information below this table. |
Irregular data are real-time using state station abbreviations, which do not match the identifier for historical data.
The vw_CDSS_GroundwaterWellsGroundwaterWellsMeasType view in HydroBase contains the metadata for well level data.
Well identifiers are used in TSTool time series identifiers as follows:
- If the view identifier column has a value, the value is used for the well identifier. Typically this is the identifier for the primary data provider.
- If the WD ID values are available, they are used.
- If the latitude and longitude are available, the location identifier is set to
LL:LatLong, where latitude is formatDDMMSSand longitude isDDDMMSS(positive value). The conversion of decimal degrees to degrees, minutes, and seconds truncates the remainder on the seconds. Subsequent reverse lookups of the well occur by querying a box around the location from the identifier and then regenerating theLL:identifier to find a match. This may result in duplicate identifiers if wells are very close together, and will generate an error. The use of the temporary identifier can be minimized by reviewing original data and ensuring that a valid identifier column value is defined in HydroBase. - If none of the above methods can be used to assign a location identifier to the time series, an error will result.
Database Views
Access to HydroBase data is provided by public views with names starting with vw_CDSS_
and stored procedures, accessible to the cdss user,
which is specified in HydroBase datastore configuration file.
Database views are used by TSTool to query time series and other data.
The views can also be queried using the
ReadTableFromDataStore command.
It is not necessary to select the database catalog or schema - just select the view to query from the provided list.
Database Stored Procedures
Stored procedures can be run using the
ReadTableFromDataStore command and will
return output similar to a table or view.
The following is a list of stored procedures, with additional documentation below.
This is not comprehensive documentation but is provided for illustration.
HydroBase CDSS Stored Procedures
| Procedure Name | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
usp_Flex |
Flexible query. | 21 fields total.
|