TSTool / Command / ChangeTimeZone
Overview
The ChangeTimeZone command changes the time zone for date/times associated with the time series.
Time zone should typically be used only with hourly and smaller time interval and
therefore this command should typically only be used for regular interval time series with interval less than a day (hour or less)
and irregular interval time series with date/time precision less than a day (hour or less).
The two main use cases for the command are:
- Set the time zone but do not shift times:
This is appropriate if the original time series did not use a time zone
but a time zone is required by later commands, such as writing to a file or database.
In some cases it is appropriate to add a time zone and in other cases remove the time zone:
- The time zone can be set by specifying
NewTimeZone. - The time zone can be removed by not specifying
OldTimeZone.
- The time zone can be set by specifying
- Set the time zone AND shift times:
Set the datet/times as in case 1 and also shift the date/time values to the new time zone,
using the offset between the old and new time zones.
For example, hour
0for time zoneAmerica/Denverwould be shifted to hour7 GMTin standard time part of the year and hour6 GMTin the daylight saving time of the year.
Time series date/times that are changed include:
- Time series start and end (and original start and end).
- For irregular time series, the date/times associated with data values.
Specification of the time zone is important for some workflows,
in particular with respect to daylight savings time,
in order to retain data integrity and properly represent the time associated with data.
For example, the time zone America/Denver indicates local time with
standard and daylight savings depending on the time of the year.
In this case, the time zone implies handling of daylight savings.
The America/Denver time zone is equivalent to -07:00 during the “standard” part of the year,
and -06:00 during the daylight savings part of the year,
meaning that local times are offset from GMT time zone by the number of indicated hours.
Consequently, using hour offsets explicitly indicates when daylight savings is in effect.
Recording original data using local time means that in the spring there will be a gap of one hour because the time is jumped forward by an hour (e.g., at 02:00 AM the clock changes to 03:00 AM), and in the fall an observation is lost because time is jumped back by an hour (e.g., at 02:00 AM the clock changes to 01:00 AM and therefore an hour is overwritten). However, if the original data are recorded using a standard time zone, then no data loss occurs. Persistent data storage (e.g., database) might use standard time (or GMT), with local time zone used for display. See:
- Daylight saving time in the United States in Wikipedia
- History of time in the United States - table listing daylight saving dates for all years
Command Editor
The command is available in the following TSTool menu:
- Commands / Manipulate Time Series
The following dialog is used to edit the command and illustrates the syntax of the command.

ChangeTimeZone Command Editor (see full-size image)
Command Syntax
The command syntax is as follows:
ChangeTimeZone(Parameter="Value",...)
Command Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
TSList |
Indicates the list of time series to be processed, one of:
|
AllTS |
TSID |
The time series identifier or alias for the time series to be processed, using the * wildcard character to match multiple time series. Can be specified using ${Property}. |
Required if TSList=*TSID |
EnsembleID |
The ensemble to be processed, if processing an ensemble. Can be specified using ${Property}. |
Required if TSList=*EnsembleID |
OldTimeZone |
The old time zone, which will be used if the time series date/time does not have a time zone. Can be specified with a processor ${Property}. Time zones should agree with the Java java.time.ZoneId. Abbreviations like MST should be avoided and more explicit zone (e.g., America/Denver) should be used to avoid ambiguity. Possible values are listed on the following site: https://garygregory.wordpress.com/2013/06/18/what-are-the-java-timezone-ids/ |
Determine from time series date/times. |
NewTimeZone |
The new time zone. Can be specified with a processor ${Property}. See the OldTimeZone description for more information. |
If blank, the time zone will be set to blank. |
ShiftTime |
Whether to shift the time numerical values in addition to setting the time zone, False or True. |
False |
Examples
See the automated tests.
The following example shows the time series before (America/Denver) and after (GMT)
for the spring daylight saving change, with the following observations:
2000-04-02 01 America/Denver(and earlier) has a 7 hour offset to2000-04-02 08 GMT2000-04-02 02 America/Denverhas a 6 hour offset to2000-04-02 08 GMT, and therefore overwrites the previous value2000-04-02 03 America/Denver(and later) has a 6 hour offset to2000-04-02 09 GMT
Note that in this example, the value for 2000-04-02 02 America/Denver might be missing in source data
because the "spring forward" would have recorded the value at hour 03.
An inverse effect will be seen converting from GMT to America/Denver.
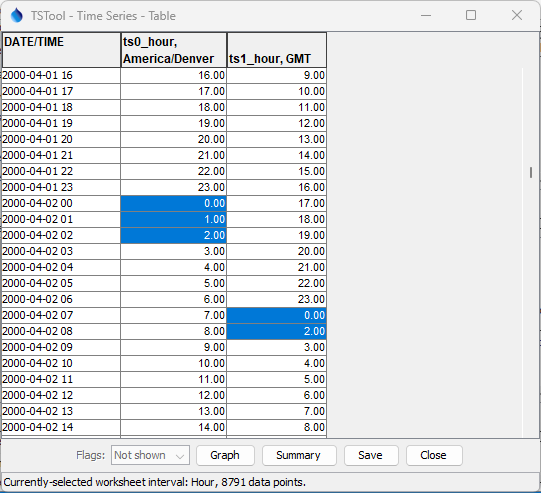
Example of "Spring Forward" Daylight Saving Change (see full-size image)
Similarly, the following example shows the time series before (America/Denver) and after (GMT)
for the fall daylight saving change, with the following observations:
2000-10-29 01 America/Denver(and earlier) has a 6 hour offset to2000-10-29 07 GMT2000-10-29 02 America/Denver(and late) has a 7 hour offset to2000-10-29 09 GMT- results in a gap at hour08 GMT
Note that in this example, the value for 2000-10-29 02 America/Denver might be recorded twice,
with the first hour lost after being overwritten.
An inverse effect would be seen converting from GMT to America/Denver.
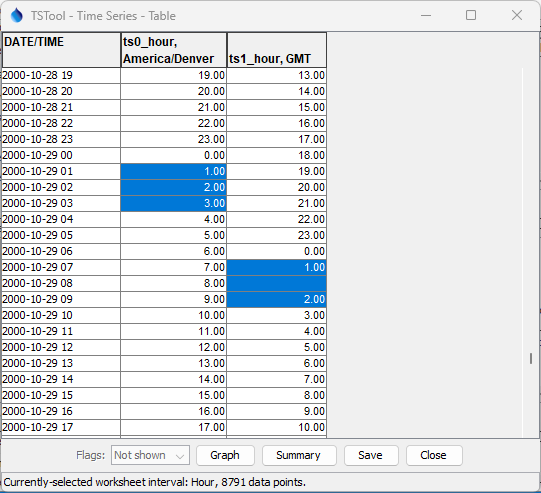
Example of "Fall Back" Daylight Saving Change (see full-size image)
Troubleshooting
See the main TSTool Troubleshooting documentation.
See Also
SelectTimeSeriescommand