TSTool / Command / WebGet
Overview
The WebGet command retrieves content from a website and writes the content to a local file.
The transfer occurs using binary characters and the local copy is the same as that shown by
View / Source (or View / Page Source) in a web browser.
This command is useful for downloading files and content from web services.
The local file can then be processed with additional commands, for example
ReadDelimitedFile if the content is comma-separated-value and
ReadTableFromJSON if the content is JSON.
The command is equivalent to an HTTP GET request.
Extraneous content (such as HTML markup around text) and inconsistencies in newline characters
(CRLF=\r\n for windows and LF=\n on other systems) may lead to some issues in processing the content with other commands.
See the TextEdit and other commands to process files after downloading.
The HTTP code is checked for the connection. If a redirect is detected, the URL for the redirect target is opened. A maximum of 100 redirects is allowed.
Zipped files can be unzipped using the UnzipFile command.
Command Editor
The command is available in the following TSTool menu:
- Commands / General - File Handling
The following dialog is used to edit the command and illustrates the command syntax.
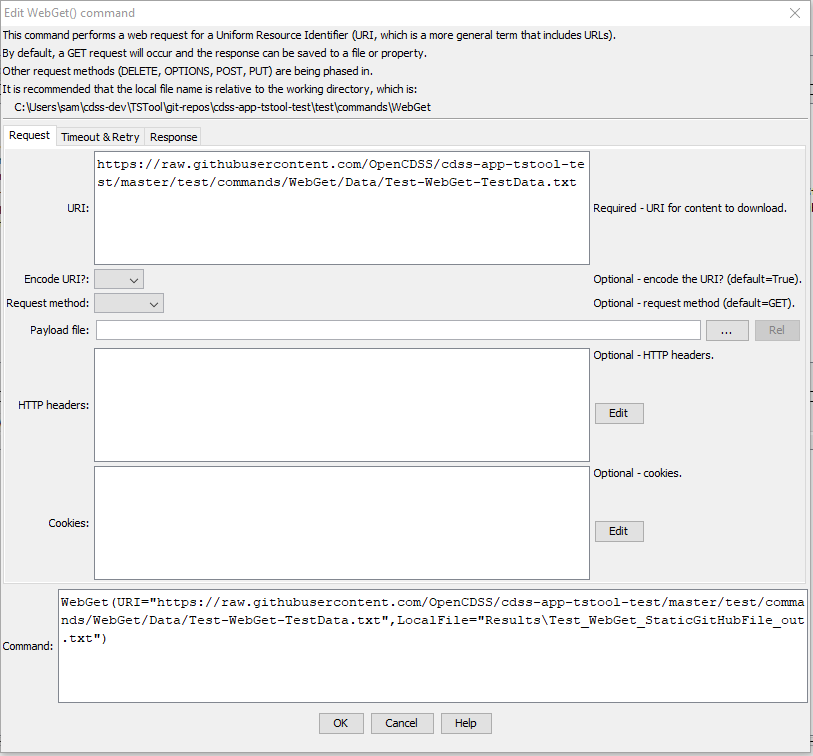
WebGet Command Editor for Request Parameters (see full-size image)
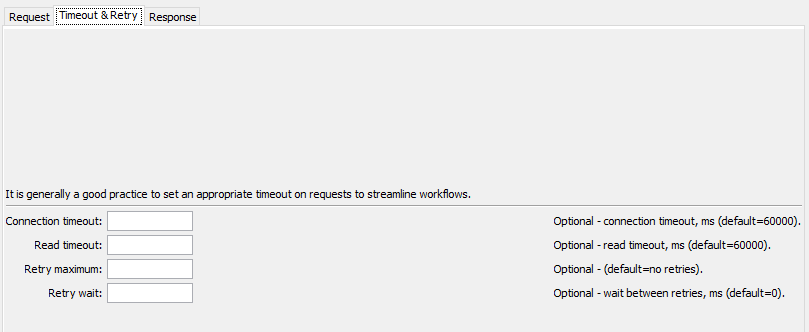
WebGet Command Editor for Timeout Parameters (see full-size image)
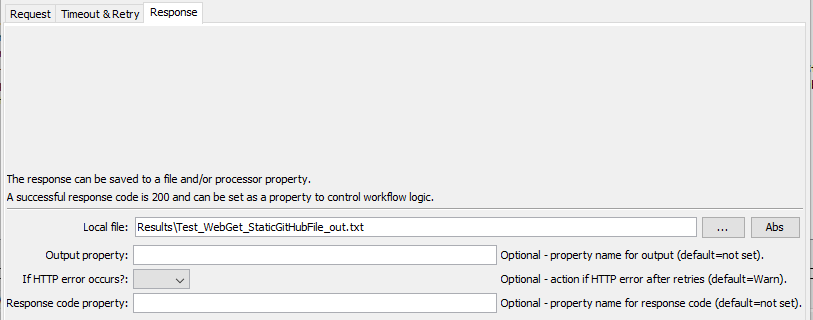
WebGet Command Editor for Response Parameters (see full-size image)
Command Syntax
The command syntax is as follows:
WebGet(Parameter="Value",...)
Command Parameters
| Tab | Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | URIrequired |
The Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) for the content to be retrieved. This is often also referred to as the Uniform Resource Locator (URL). Global properties can be used with the ${Property} syntax. The URI can include query parameters with special characters such as equal sign because URLs can be encoded (see the EncodeURI parameter). |
None - must be specified. |
EncodeURI |
Indicate whether to encode the URL to protect special characters: False or True. See Percent-encoding on Wikipedia. Encoded URLs are difficult to read and therefore human-readable URL can be entered as the URI, such as using spaces. However, the requested resource may require encoding to be recognized by a called service. If the provided URI is already encoded, then specify False. Only the value part of ?property=value and &property=value query is encoded. |
True |
|
RequestMethod |
The HTTP request method:
|
GET |
|
PayloadFile |
Payload file for PUT and POST requests. |
||
HttpHeaders |
List of HTTP header properties to be attached to the request. This is useful if a website requires authentication via a key property, and for testing. The format is PropertyName1:PropertyValue1,PropertyName2:PropertyValue2,... |
No headers. | |
Cookies |
List of HTTP header cookie properties to be attached to the request. The format is CookieName1:CookietValue1,CookieName2:CookieValue2,... |
No cookies. | |
| Timeout | ConnectTimeout |
The connection timeout in milliseconds. If a connection has not occurred in this time, an error will result. | 60000 (60 seconds) |
ReadTimeout |
The read timeout in milliseconds. If data read has not started in this time, an error will result. For example, a connection may be established and the server may begin processing a response, but may not provide data to read. | 60000 (60 seconds) |
|
RetryMax |
Maximum number of retries, useful when a server rejects connections or is known to experience downtime. Using retries will cause the workflow to wait on this command. Another option is to use the For command to control retries. |
Try one time. | |
RetryWait |
Wait time in milliseconds before retries, which is additional time that can be used in addition to ConnectTimeout and ReadTimeout to space retries. |
0 |
|
| Response | LocalFile |
The local file in which to save the content. Global properties can be used with the ${Property} syntax. |
Output file will not be written. |
OutputProperty |
Name of the processor property to set the retrieved contents. For example, a snippet of data can be set as a property for processing by other commands, in which case the content will be accessed using ${Property} notation. |
Content will not be set in a property. | |
IfHttpError |
Indicate how to handle an HTTP return code other than 200:
|
Warn |
|
ResponseCodeProperty |
The HTTP response code returned by the request. This can be used to check whether the request was successful and control the workflow. Code 200 typically indicates success. |
Property value is not set. |
Examples
See the automated tests.
Checking for Valid URLs
This WebGet command can be used to check a dataset for valid URLs.
For example, if the dataset can be represented as a table:
- Use the
Forcommand to iterate through the table rows. Use theTablePropertyMapcommand parameter to set a processor property for the website URL. - Use this
WebGetcommand with the following parameters:URI- for the URLHttpHeaders- if necessary, set theUser-Agentheader to a suitable agent (see Chrome web browser user agent or Mozilla User-Agent documentation) to mimic a web browser because some websites may reject requests without an accepted user agent. Edit the user agent value to remove commas, which cause problems parsing the parameter. It may also be necessary to surround the user agent property value with single quotes.ResponseCodeProperty- set a processor property for the HTTP response code
- Use the
IfandMessagecommands to check the error code. Any value other than 200 can be considered to be an error and a warning or failure message can be generated.
Any warnings or errors should be reviewed and problem URLs should be corrected in the dataset.
Troubleshooting
See the main TSTool Troubleshooting documentation.